The Ever Evolving Hanshin Port
At Hanshin Port (Kobe Port and Osaka Port), as the International Container Strategic port, we are working to promote the further improvement of productivity and user convenience through the strengthening of container terminal functions and through a digital transformation in the port. We are also promoting terminal operations that will be resilient in the face of natural disasters and all other risks, the enhancement and maintenance of ferry and liner functions that will lead to higher logistics efficiency, and also measures for the formation of a carbon neutral port (CNP).

Main initiative examples
- Container terminal redevelopment promotion
- CONPAS introduction to improve gate convenience
- Formation of a carbon neutral port (CNP) through hydrogen fuel
- LNG bunkering for reduced environmental burden
- Use of AI for preventive maintenance on gantry cranes
- Strengthening of disaster prevention functions in light of typhoon damage
- Investment overseas (Sihanoukville Autonomous Port, Cambodia)
- Cargo creation business: Osaka Port support for food exports
Container terminal redevelopment promotion
We are working to improve convenience by promoting redevelopment aiming for a “container terminal where transportation is possible ‘regularly’ and ‘speedily’,” which is what is demanded by port users.
- Development policy
- – Promoting the development of a high-standard container terminal with deep water (16 m) to respond to the increasing size of container ships
- – Promoting the integrated use of the container terminals for the more effective use of facilities, and improving the connectivity of international cargo and domestic cargo to enhance transshipment functions
- – The improvement of productivity to realize efficient terminal operations in a high-standard container terminal

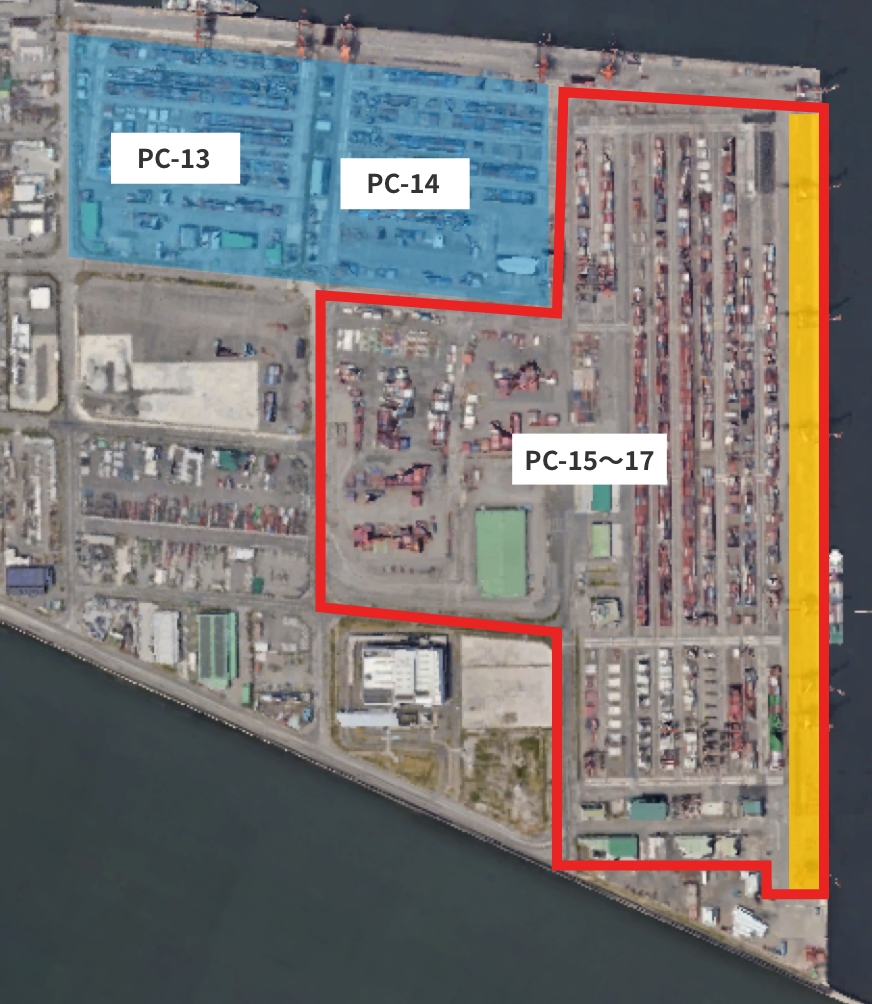
Redevelopment work in the Kobe Port Port Island (Phase 2) area (KICT)
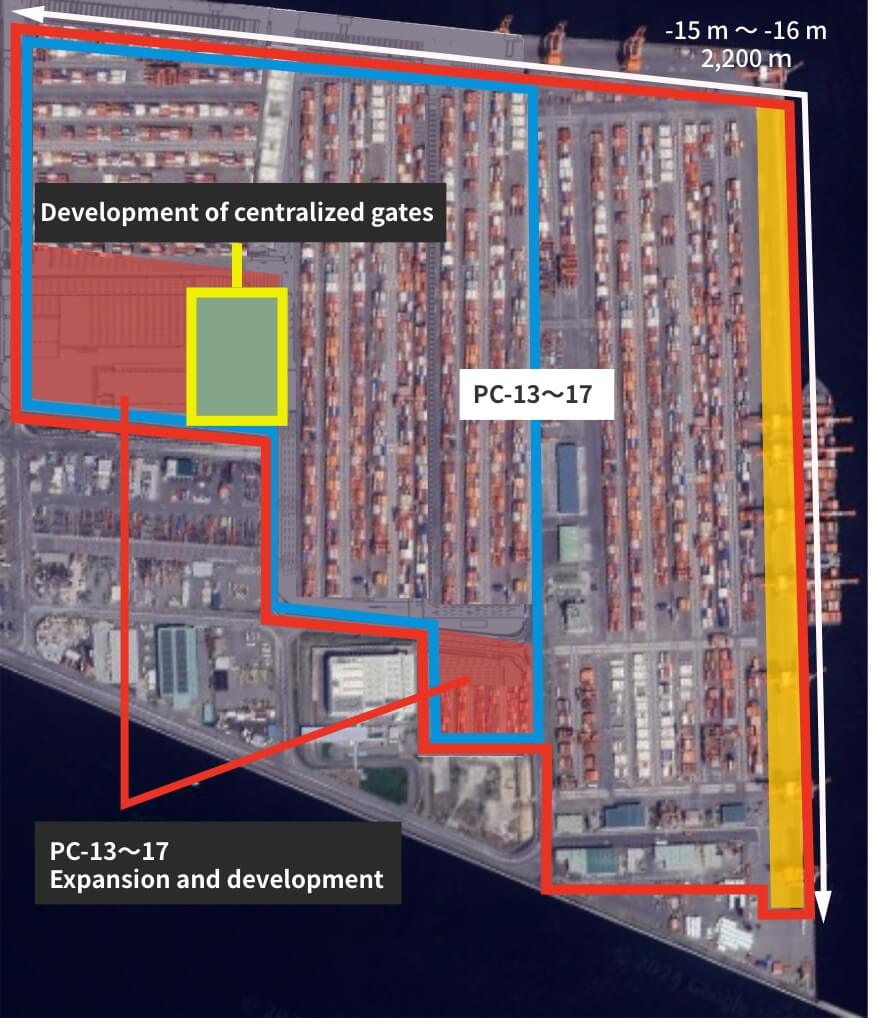
■ Redevelopment of PC-13 to 17
We will reorganize the container terminal to develop one of the largest high-standard container terminals in Japan, with water depths of 15 m to 16 m and a total quay wall length of 2,200 m. We will also develop a common gate and introduce a CONPAS system (planned). The plan is to prepare electrically driven remote RTG* for the yard in order to improve the working environment, to improve the efficiency of the cargo handling, and to reduce the burden on the environment.
- *RTG: Rubber Tired Gantry crane
Before redevelopment
©Google Earth
After redevelopment (planned completion during fiscal 2025)
©Google Earth
- Quay wall with water depth 16 m
- Expanded area
- Redeveloped area

Centralized gates

CFS (Container freight station)

Packaging shed
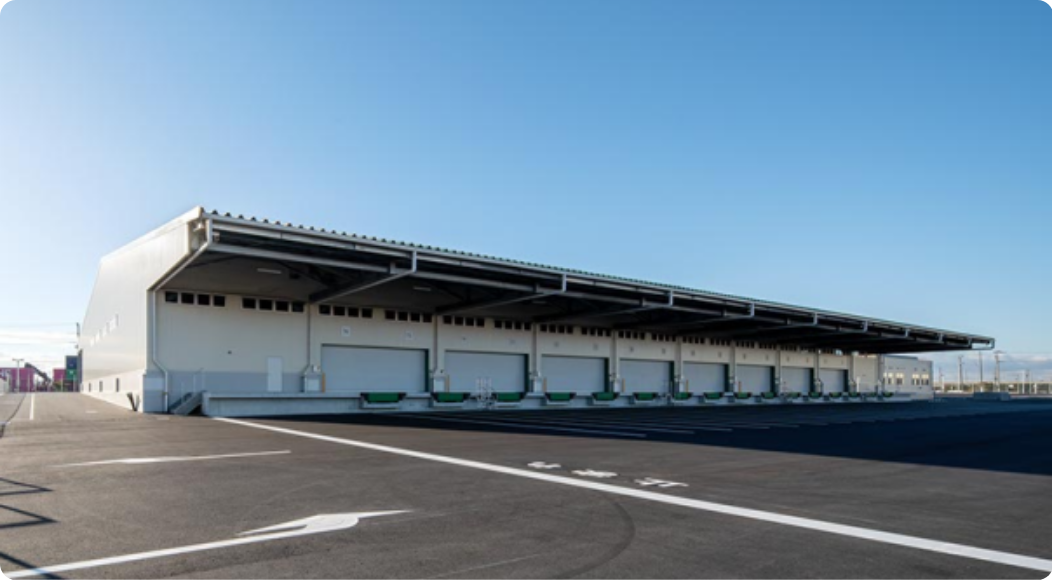
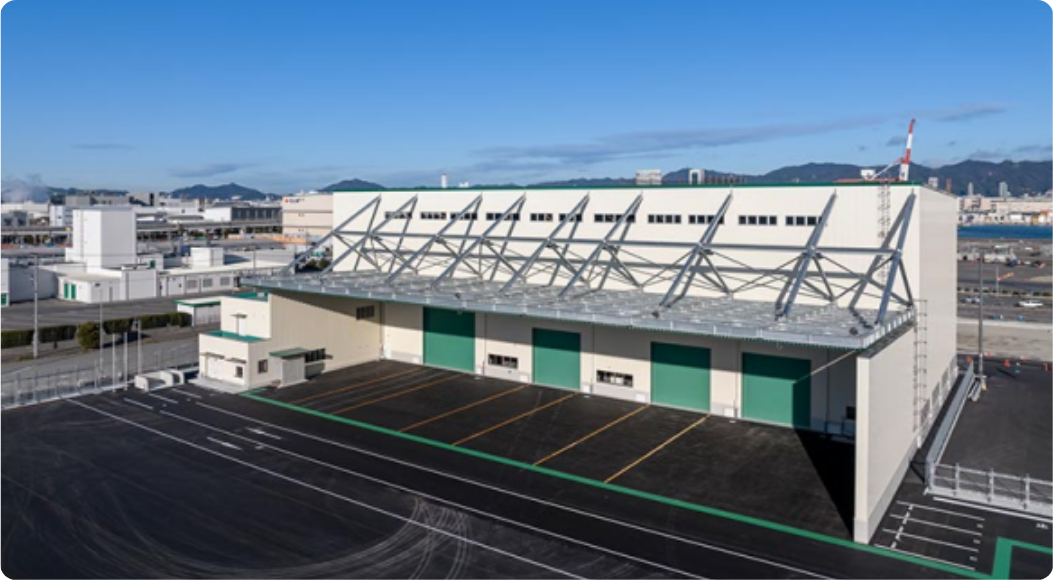
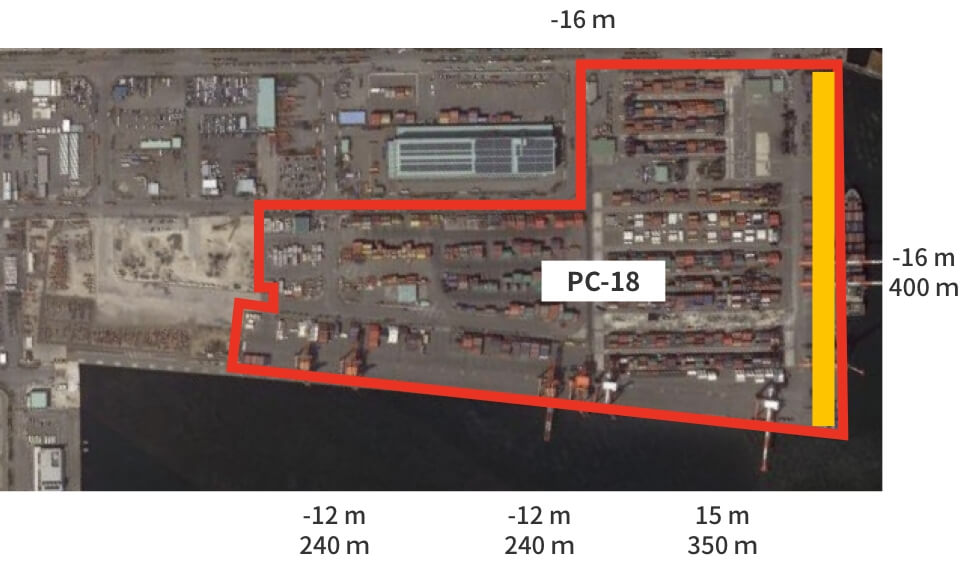
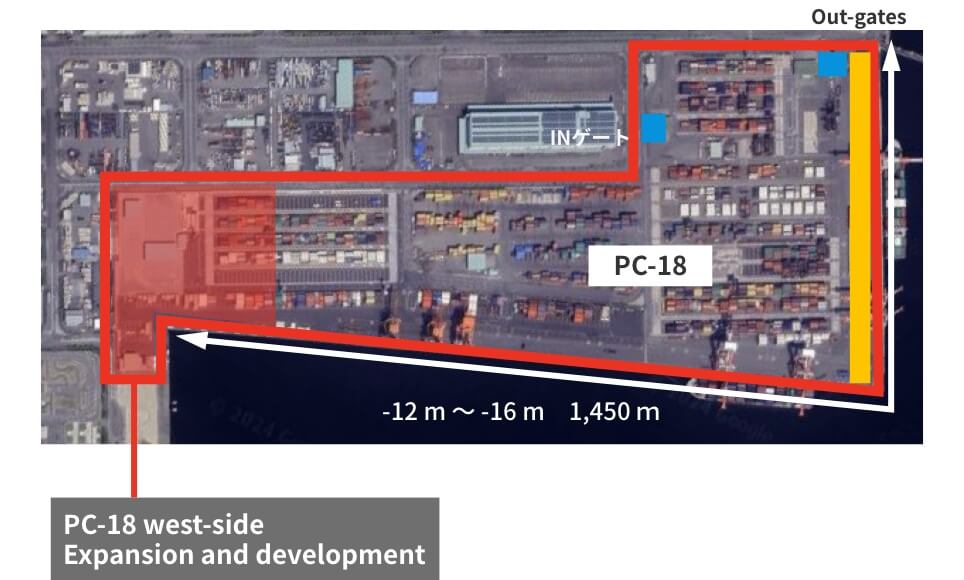
■ Redevelopment of PC-18
For PC-18, we will expand the west side and redevelop the terminal as a large-scale high-standard container terminal to promote more efficient terminal operation. (Yard expansion, increased number of gates, etc.) We will also introduce the CONPAS system to enable smooth gate passage, improve terminal productivity, and reduce the burden on the environment by easing congestion. In addition, the plan is to prepare remote RTG for the yard in order to improve the working environment and to improve the efficiency of the cargo handling.
Before redevelopment

©Google Earth
After redevelopment
©Google Earth
- Quay wall with water depth 16 m
- Expanded area

Photograph of completed PC-18 west-side expansion
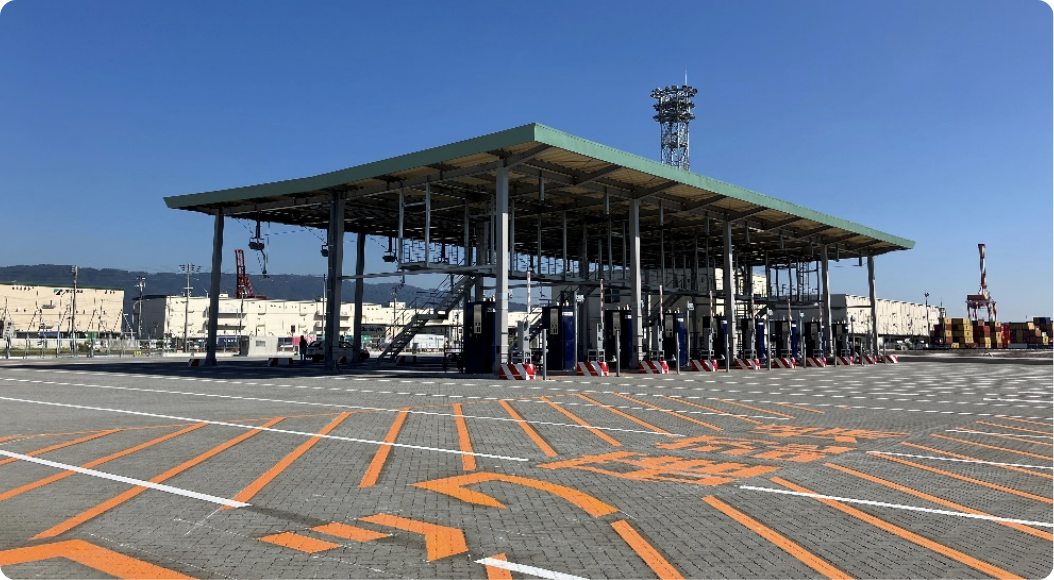

In-gates

Out-gates
Kobe Port Rokko Island area redevelopment work
We are converting the yards for the coastal feeder service berths to transfer cranes to promote the integrated use for domestic and international services.
Before redevelopment
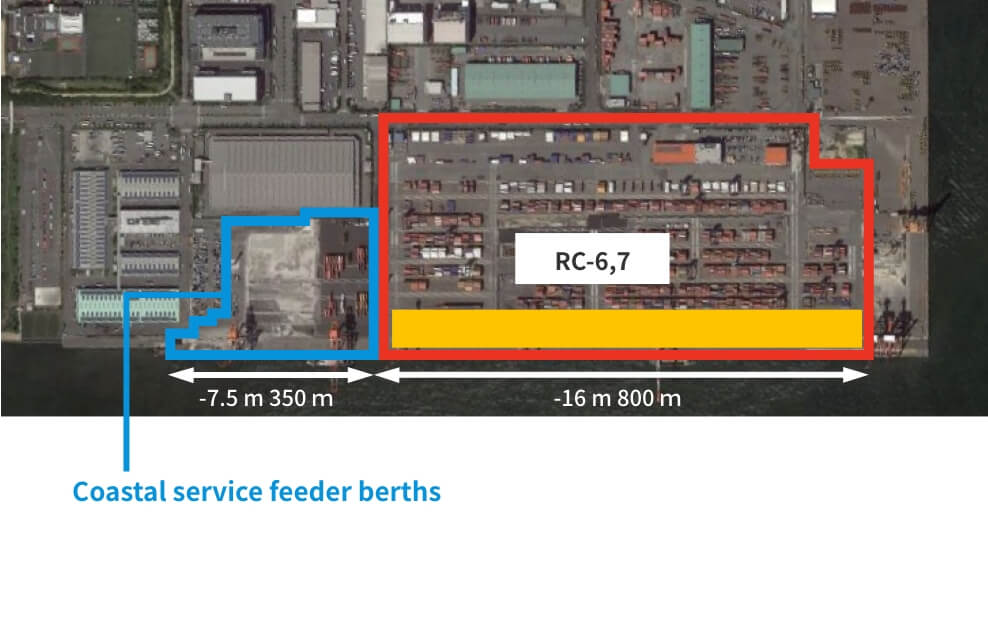
©Google Earth
After redevelopment
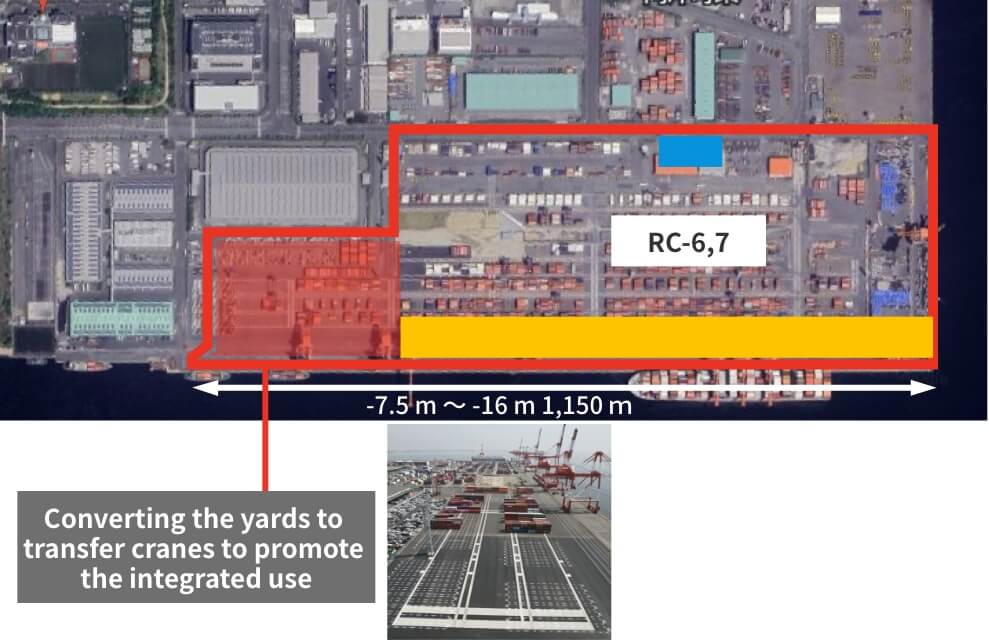
©Google Earth
- Quay wall with water depth 16 m
- Expanded area
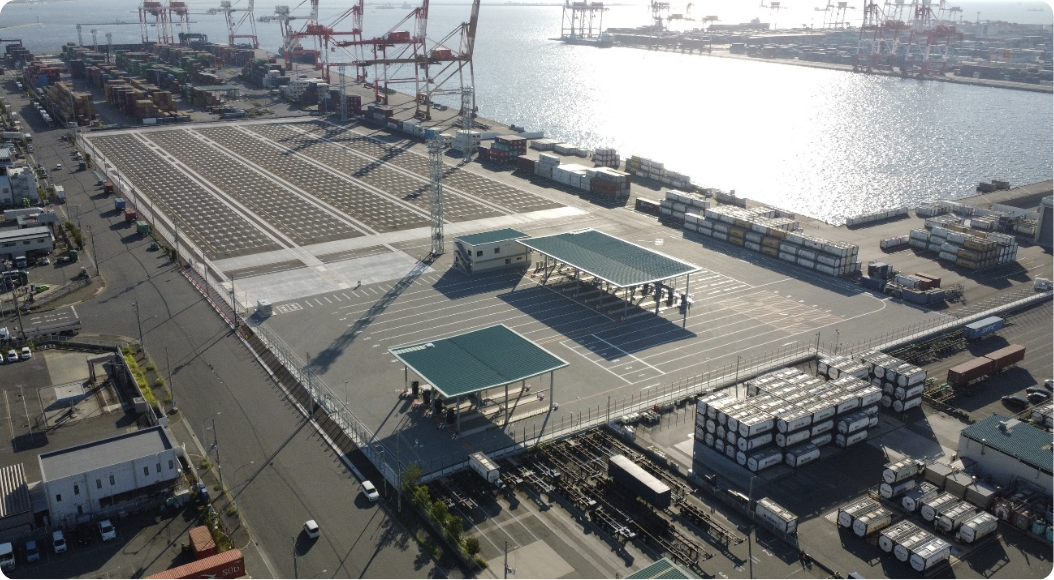
Osaka Port Yumeshima area redevelopment work
■ Osaka Port: Redevelopment of C-10 to 12
To enhance the functions of the container terminals in the Osaka Port Yumeshima area, we will implement measures such as yard expansion, an increase in the number of gates and an enlargement of gantry cranes. In particular, we will newly develop the terminal gates as common gates for a large-scale high-standard container terminal and introduce the CONPAS system. The aim of this is to realize smooth gate passage and improved terminal productivity, and to reduce the burden on the environment by easing congestion.
Before redevelopment
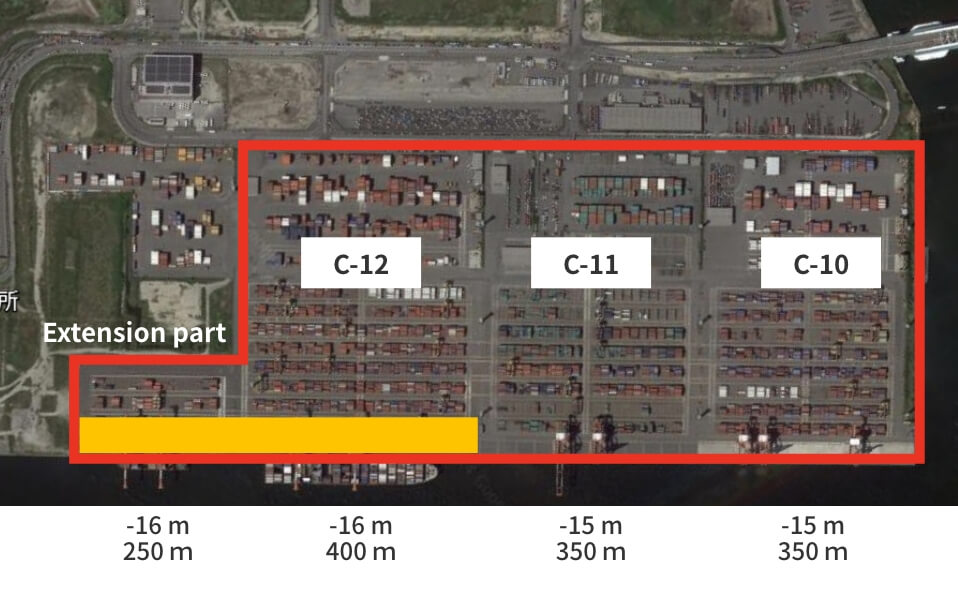
©Google Earth
After redevelopment
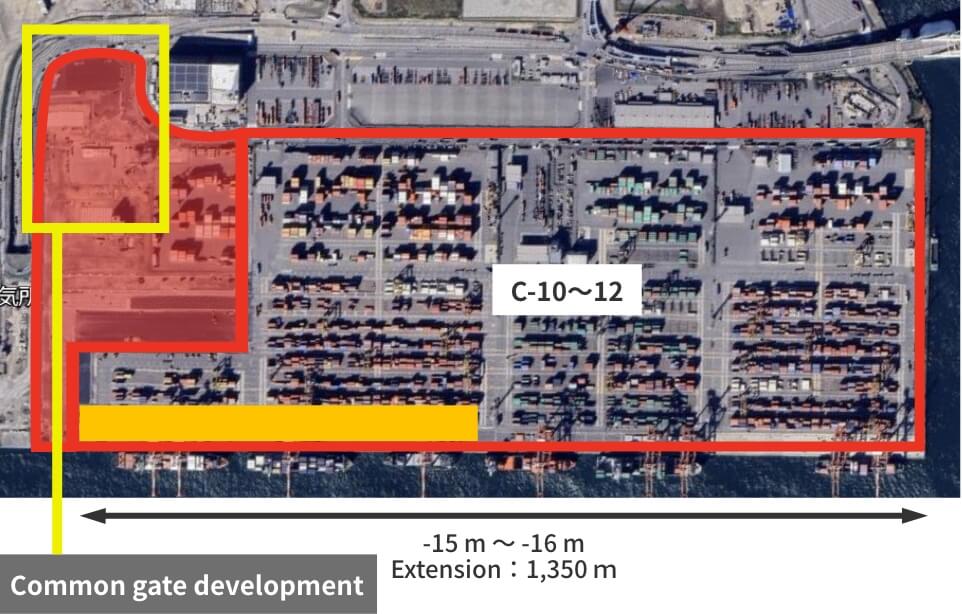
©Google Earth
- Quay wall with water depth 16 m
- Expanded area
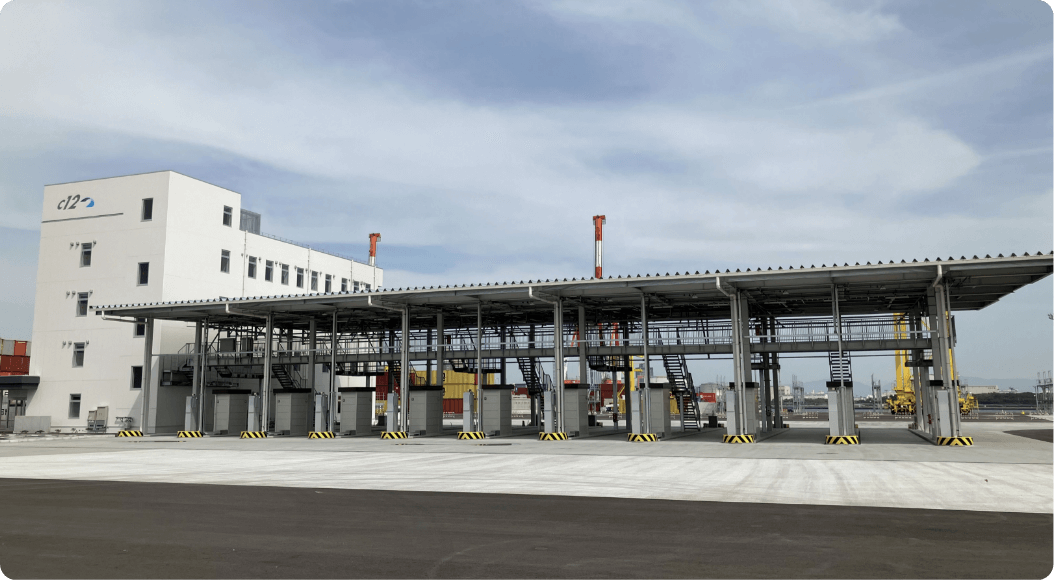
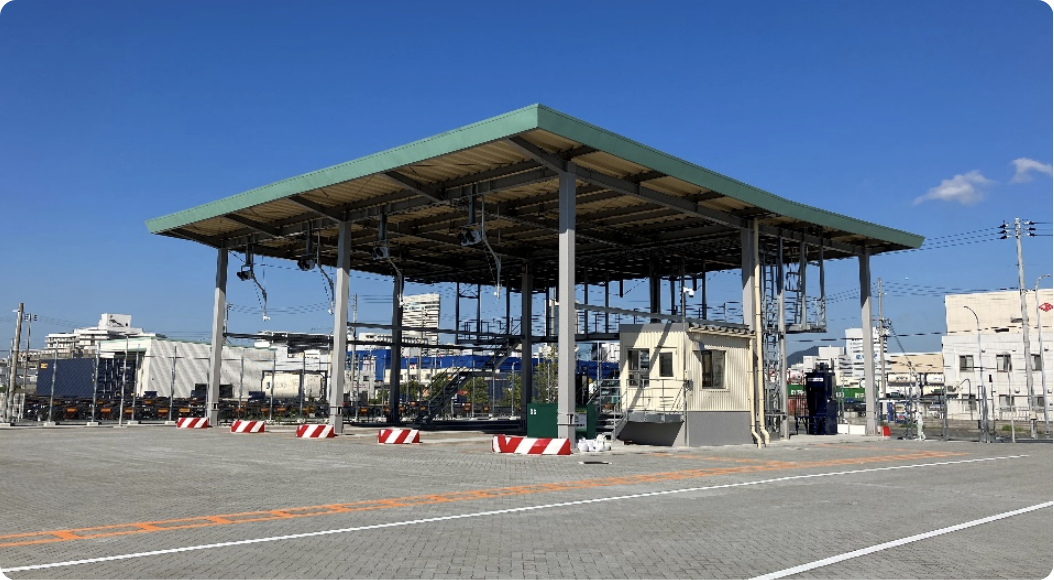
Administrative building and in-gates

Out-gates
CONPAS introduction to improve gate convenience
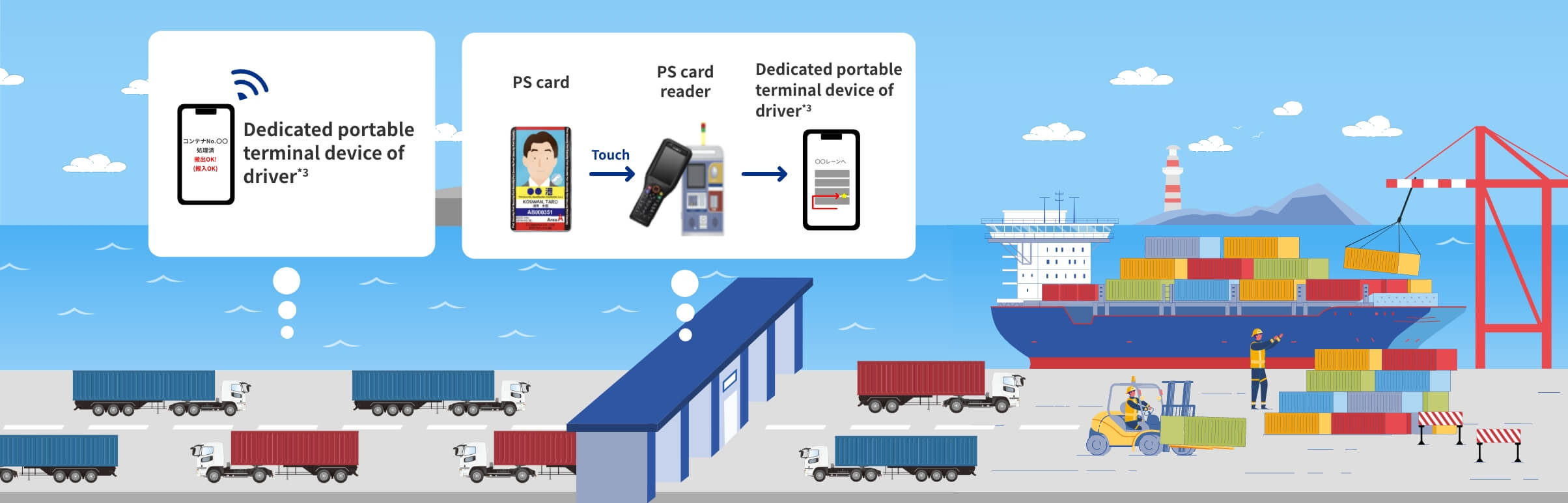
CONPAS*1 is a system that was developed by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism with the aims of eliminating the congestion before the gates in a container terminal and reducing the time spent at the terminal by container trailers, to improve the efficiency of container transportation and to increase productivity. With the aim of improving convenience, Hanshin Port has introduced items such as portable terminal devices dedicated to CONPAS, as original functions of Hanshin Port. The operation of this began from March 29, 2024 in the Osaka Port Yumeshima Container Terminal and from September 27, 2024 in Kobe Port PC-18. Consideration of an introduction to the other terminals is ongoing.
Outline of CONPAS at Hanshin Port
Expected effects*2 and results of trial operations
(1) Carry-out/Carry-in reservations
The smoothing of trailer arrival times through the introduction of a reservations system
(2) Prior checks of carry-in/carry out information
The avoidance of trouble at the gates through prior checks of the carry-out information and collation of the carry-in information
(3) Utilization of PS cards* and portable terminal devices
Reduction of the processing time at gates through PS card touch processing and destination displays on portable terminal devices*3
- *PS card: An identification card issued by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism to enable the smooth checking of entrance into international terminal facilities
(4) Utilization of reservation information and vehicle approach information
The improvement of yard processing efficiency through the utilization of vehicle information, etc., through CONPAS

Harbor roads
Results of trial operations
- ・Through measures such as the reservation system and the establishment of lanes only for CONPAS, almost all of the CONPAS vehicles arrived at the container terminal gate at the reserved time
- ・The time that CONPAS vehicles spent waiting before the gate for the Osaka Port DICT (actual carry-in and carry-out) was reduced by an average of 30 minutes compared to normal vehicles
- *5th trial operation at Osaka Port DICT and 4th trial operation at Kobe Port PC-18 (July to August, 2023)
Further future development
Work to expand the use of CONPAS while aiming to level out the trailer arrival times
Gates
Results of trial operations
- ・Gate processing times (actual carry-in/carry-out) were reduced by around one minute on average
- ・No waiting of CONPAS vehicles at gate due to carry-in form errors, etc.
- *2nd trial operation at Osaka Port DICT (August to September 2022)
- *2nd trial operation at Kobe Port PC-18 (August to September 2021)
- *5th trial operation at Osaka Port DICT and 4th trial operation at Kobe Port PC-18 (July to August, 2023)
Further future development
Work to expand the functions of CONPAS for more efficient gate work
Yard
Results of trial operations
- ・Construction of a data transmission function to send CONPAS reservation information, etc., to the terminal operation system
Further future development
Collaboration with terminal operating companies, etc., to aim to improve the efficiency of yard work through the use of CONPAS reservation information
- *1. Abbreviation of Container Fast Pass
- *2. Includes the expected effects of the measures for functional enhancement after the start of operations, and the expected effects of the coordination with other systems
- *3. Original function of CONPAS at Hanshin Port
Schedule for CONPAS introduction (Planned)

Formation of a carbon neutral port (CNP) through hydrogen fuel
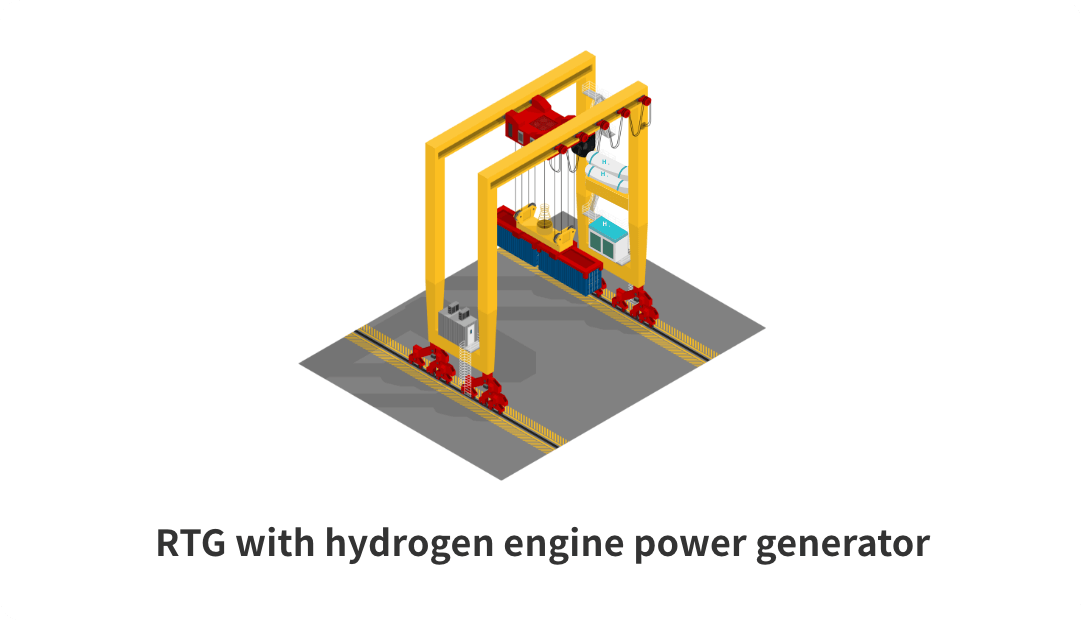
There are increasing expectations for the use of the clean energy source hydrogen for the realization of a decarbonized society. Hanshin Port is also promoting the formation of a carbon neutral port (CNP) through measures such as the introduction of more sophisticated port functions and the development of the environment for receiving hydrogen. As one part of this, it was decided that the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism would perform an on-site demonstration of the introduction of hydrogen energy to port cargo handling machinery and a group of companies led by HPC will implement the conversion of an RTG diesel engine power generator at the Kobe Port to a hydrogen engine power generator. In addition, we are also working on achieving zero emissions for the port operations through measures such as shifting to hydrogen fuel and electrification on cargo handling machinery.
Conversion of cargo handling machinery
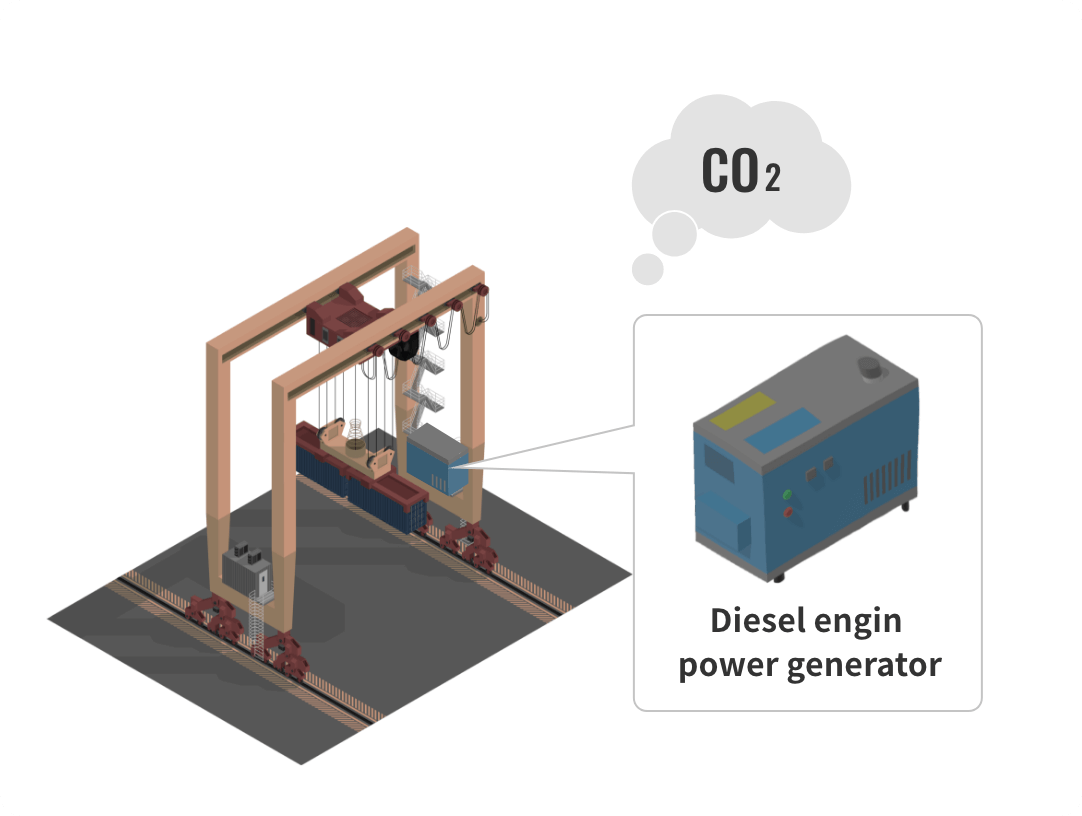
Currently operated using a diesel engine power generator
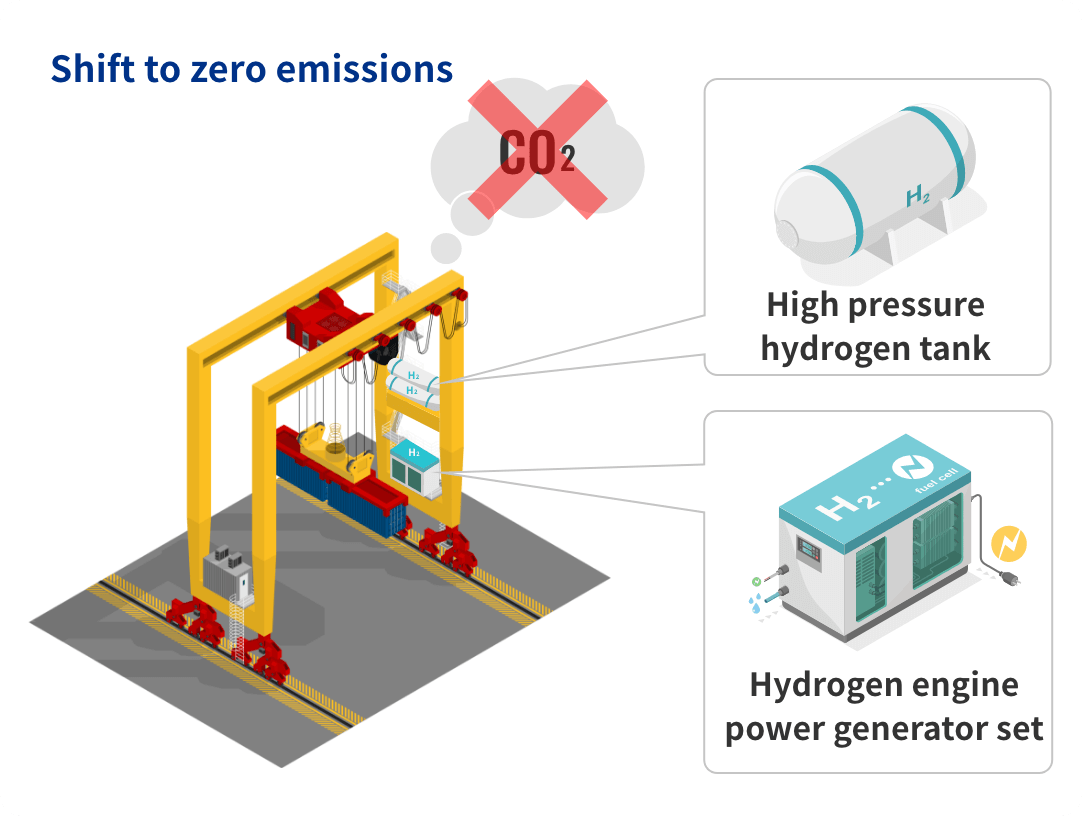
Conversion to a hydrogen engine power generator for operation using hydrogen as a fuel
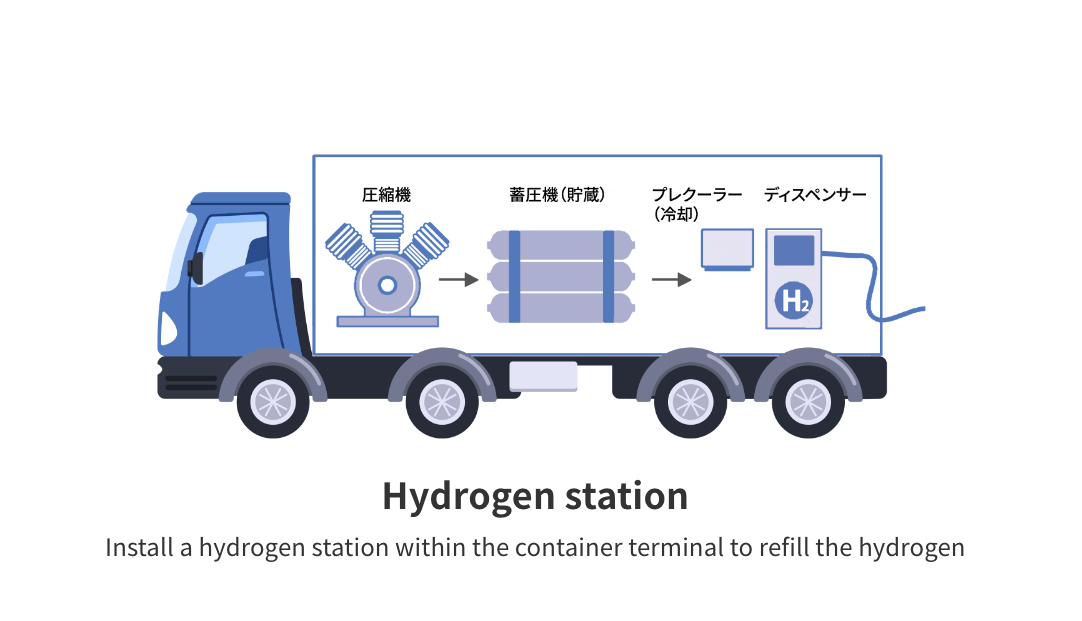
Hydrogen supply and refilling

LNG bunkering for reduced environmental burden
In connection with the strengthening of international regulations on the exhaust gases from marine vessels, increasing importance is being placed on bases that can supply fuel to LNG fueled vessels, which have a smaller impact on the environment.
Hanshin Port is participating in the LNG bunkering* (liquefied natural gas fuel supply) business for marine vessels using the ship to ship method*. Through the LNG bunkering, the port is coordinating communication with the national government, port management body and port-related personnel, etc., and is working to attract LNG vessels and to promote the spread of LNG fuel use on marine vessels. This will contribute to the future growth and development of Hanshin Port.
- *LNG bunkering: The act of supplying liquefied natural gas (LNG) to marine vessels as fuel. A dedicated ship called the bunkering vessel supplies LNG to refuel vessels moored at a quay and vessels stopped in anchorage areas
Business scheme
 Details of business
Details of business
Use of AI for preventive maintenance on gantry cranes
In order to prevent the occurrence of sudden failures on gantry cranes*, we are analyzing the cause and effect relationship between data such as gantry crane operation log data accumulated in the cloud and actual sudden failures that have occurred in the past, and are advancing the construction of a failure prediction model using AI. The development is ongoing so that it will be possible to grasp any signs of gantry crane failure or abnormality and become possible to perform inspections and repairs on the gantry cranes before any sudden failure occurs.
- *Gantry crane: Extremely large cargo handling machinery used to lift the containers carried on ships onto land and to load containers from the land onto ships, with a structure that can move on rails

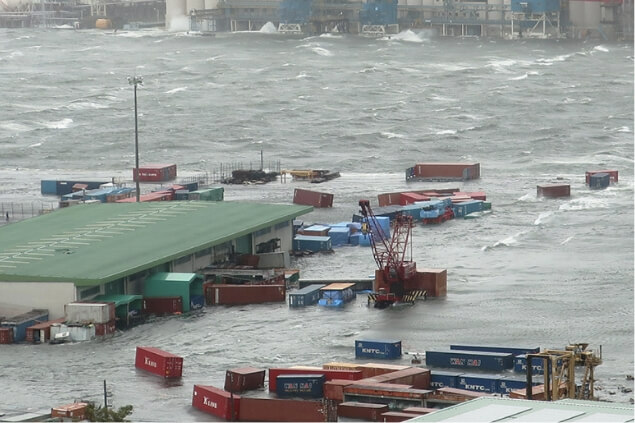
Strengthening of disaster prevention functions in light of typhoon damage
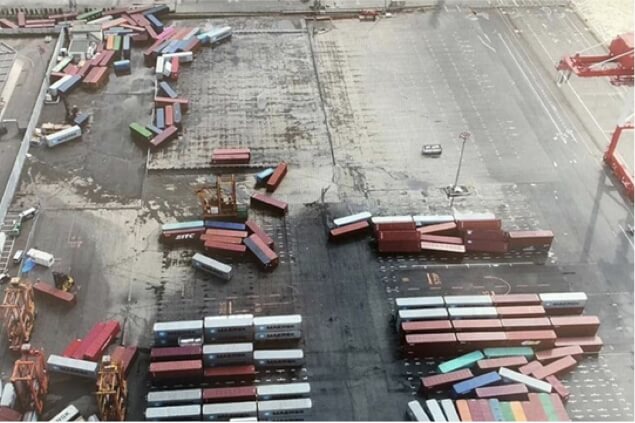
As a result of Typhoon Jebi in 2018, both the Kobe Port and Osaka Port experienced record-high tide levels and suffered great damage such as containers flowing out to sea due to the flooding of the terminals.From the viewpoint of preventing a repeat disaster, we have worked with the national government and port management body to implement raising work and power outage countermeasures.
Situation of damage


Countermeasure work in the container terminals, etc.
Also secure sufficient height to withstand a tsunami from a Nankai or Tonankai trough earthquake
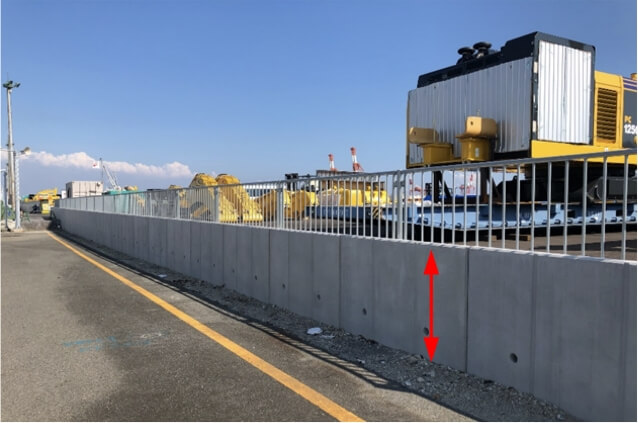

Raising of yard as flooding countermeasure
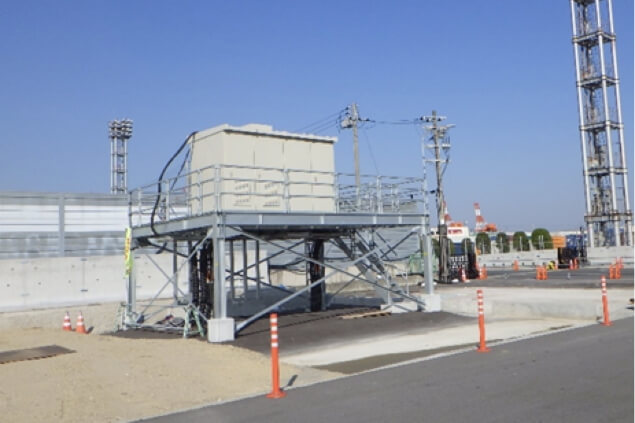

Raising of electric power supply facilities (Container terminal)
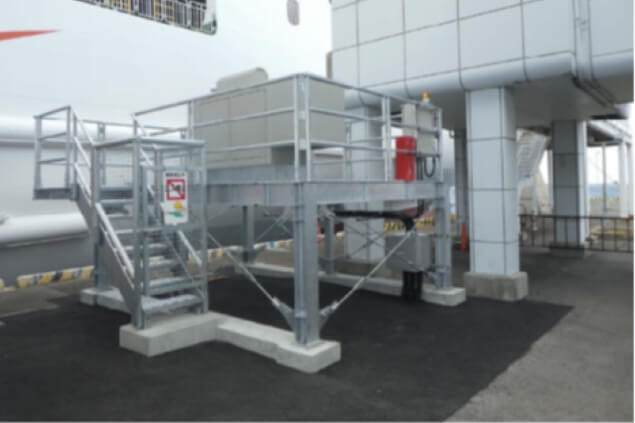

Emergency power generation facilities (Ferry terminal)
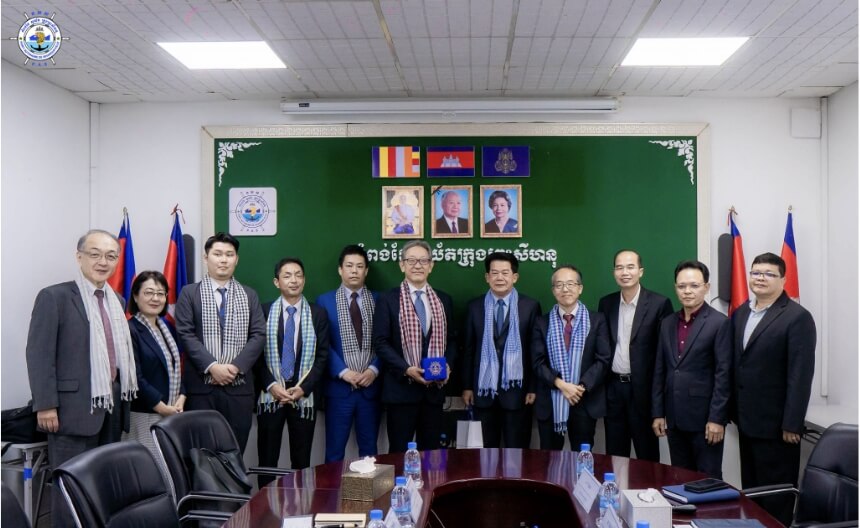
Investment overseas (Sihanoukville Autonomous Port, Cambodia)
In December 2018, HPC acquired some of the shares of the company managing and operating the Sihanoukville Autonomous Port, the only deep water port in Cambodia. We have promoted a strengthening of the relationship through steps such as implementing study tours of Hanshin Port, the provision of knowledge related to cargo handling machinery, etc., and the provision of advice related to port planning. We began technology exchanges from fiscal 2022.
Visit to Sihanoukville Autonomous Port (December 2023)


Sihanoukville Autonomous Port employee training at Hanshin Port (February 2024)


Cargo creation business: Osaka Port support for food exports
We are promoting the establishment of logistics facilities by private business operators within Hanshin Port, with parties such as the port management body playing a central role, and also utilizing the cargo creation support system of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. From the perspective of “creating new cargo,” we are coordinating with the port management body and actively promoting the “exporting of food” promoted by the government.

Establishment of a cargo collection incentive system for agricultural, forestry and fishery products and food, etc., using reefer containers, etc.
We conduct support business using incentives, such as a project to attract mixed-load reefer export services for the NVOCC* companies offering mixed-load reefer export services, and a logistics improvement project aimed at cargo owners and logistics businesses. See below for details of the business.
- *NVOCC: Abbreviation of Non Vessel Operating Common Carrier. These are operators that do not have their own transportation means such as marine vessels, but use the vessels of shipping companies to transport cargo.
Support for the matching of Japanese suppliers with overseas buyers through participation in exhibitions and the hosting of business negotiations
In order to promote the exporting of agricultural and fishery products and food, etc., from Osaka Port, we are receiving cooperation from related institutions and are participating in exhibitions and hosting business negotiations. In order to support suppliers in the development of new sales routes through negotiations with overseas buyers via local trading companies, the local trading companies invite overseas buyers from various locations, including China, Hong Kong and Singapore, and then business negotiations are held with suppliers selected through a public appeal for participation.






